The ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas in the Middle East has extensive implications for various facets of international relations, including economics and trade. One notable area facing impact is the global logistics and supply chain industry. The disruption in the supply chain is expected to result in increased logistics costs, particularly affecting shipments of agricultural commodities that use this route. Consequently, this disruption is likely to lead to higher commodity prices.
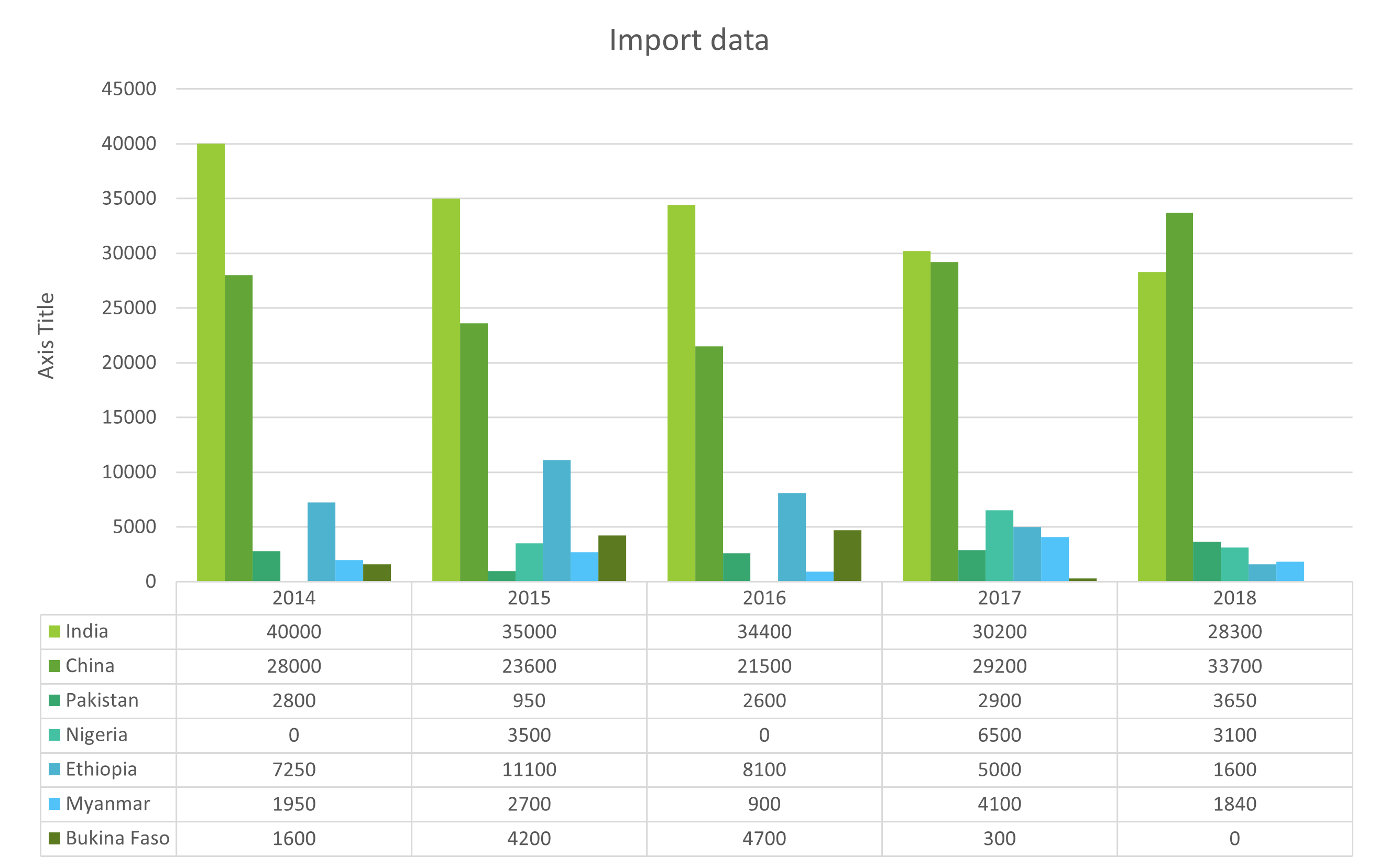
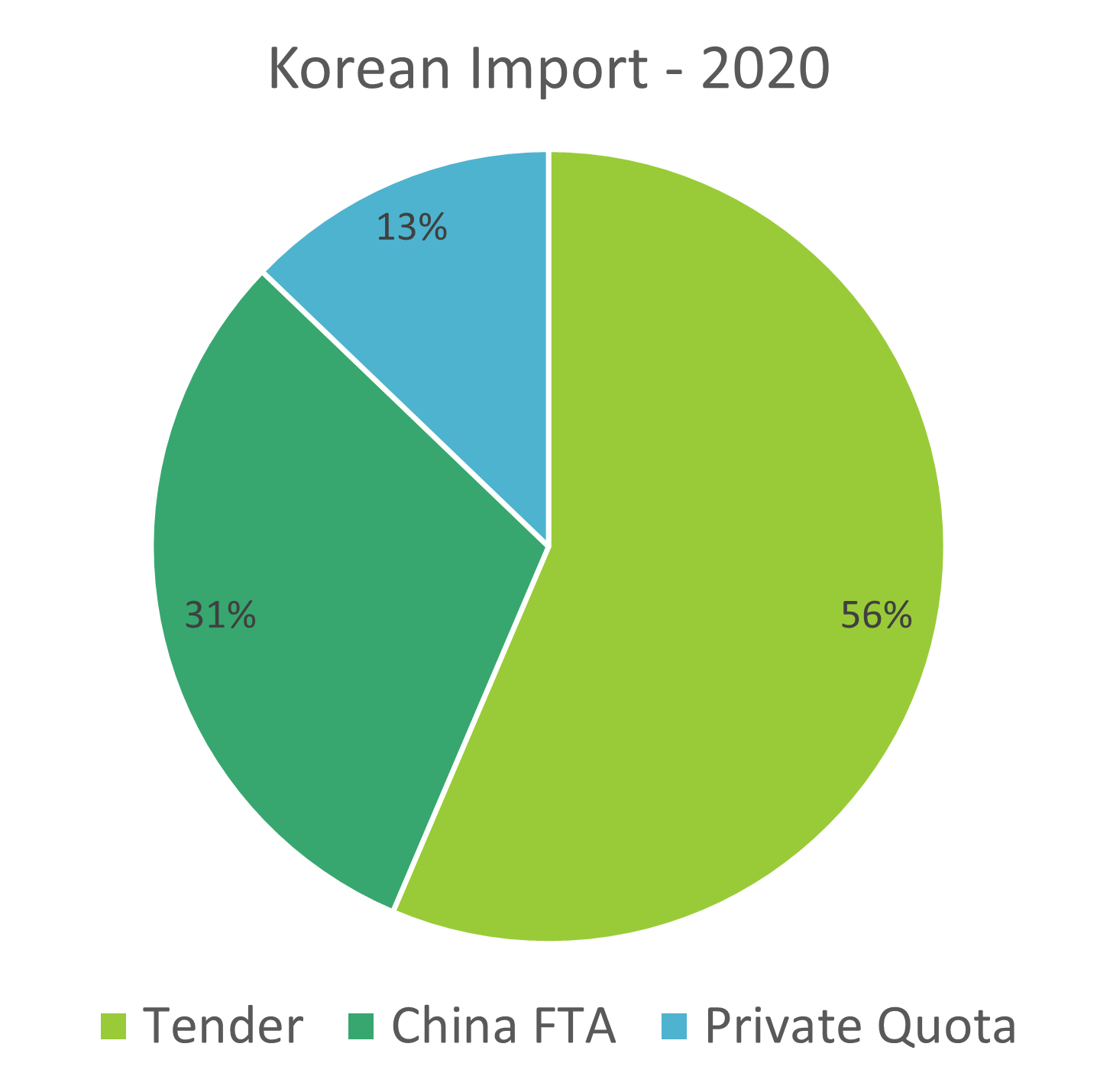
And the same goes with Egypt as well. Egypt’s heavy dependence on sesame imports, primarily sourced at 86% from Sudan in 2022, has encountered significant disruptions due to the ongoing Sudanese conflict since April 2023. This disturbance has had a profound impact on Egypt’s sesame seed supply. Given the ongoing challenges in Sudan’s sesame seed production and the influx of Sudanese migrants to Egypt due to the conflict, there is an expected surge in Egyptian sesame seed imports. This situation underscores the importance for Egypt to explore alternative sources beyond Sudan. Notably, India and Brazil have demonstrated increased export activity to Egypt in 2023. India experienced a year-on-year increase of 27.06%, exporting 3,311 metric tons of sesame seeds to Egypt from January to July 2023, while Brazil’s exports saw a remarkable 189% year-on-year surge, reaching 2,432 metric tons from January to October 2023. Despite Egypt’s efforts to boost local sesame production, we predicts a continued absence of Sudan’s sesame market, exerting an influence on the Egyptian sesame seed industry. Consequently, Egypt must effectively diversify its sourcing channels to enhance sesame supply in 2024.
Sesame seeds hold a crucial position in Egyptian cuisine and culture, frequently featured in a variety of dishes that appeal to all segments of the population. Egypt’s annual local consumption of sesame seeds amounts to 100,000 metric tons (mt), with a substantial 75% utilized in the production of Tahini and Halva. This underscores the noteworthy dependence on sesame seeds in the creation of staple Egyptian food products.
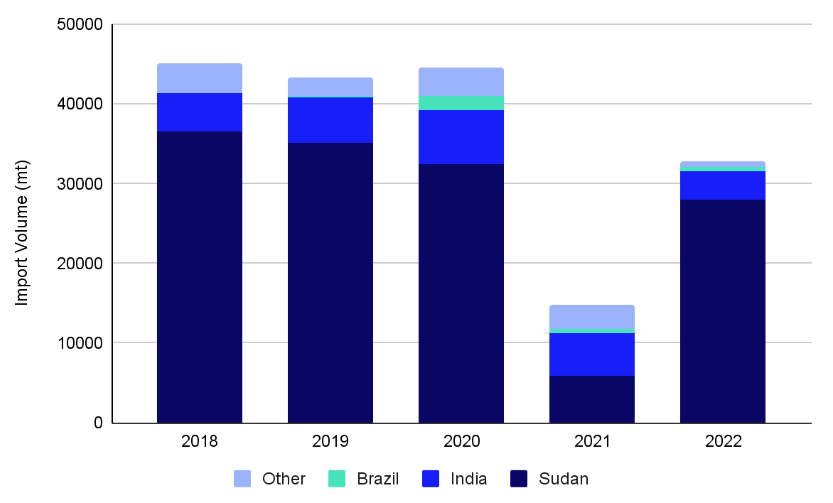
Nevertheless, Egypt’s annual domestic sesame production, estimated at 30,000 metric tons, falls significantly short of meeting the market’s demand of 100,000 metric tons. As a result, Egypt heavily depends on sesame imports, with a substantial 86% sourced from Sudan in 2022. In 2021, Egyptian sesame seed imports experienced a decline due to reduced supply from Sudan following a military coup in October. Despite this, the close proximity between Egypt and Sudan facilitates easy transportation, and Sudanese sesame, renowned for its quality, remains the primary choice for most Halva and Tahini factories in Egypt.
However, the conflict in Sudan since April 2023 has severely disrupted Egypt’s sesame supply chain. Traditionally a key global supplier, Sudan has faced challenges, leading to shortages in the Egyptian market and a subsequent rise in prices. This scarcity has notably impacted processed Halva and Tahini production in Egypt, resulting in a price increase for Halva to EGP 74.67 per kilogram in May 2023, representing a 9% month-on-month increase.
In response to these supply chain vulnerabilities, the Egyptian Government aims to enhance sesame cultivation. The Ministry of Agriculture plans to increase sesame cultivation areas to 150,000 acres by 2024, marking a significant 60% year-on-year increase, with the goal of strengthening local production.
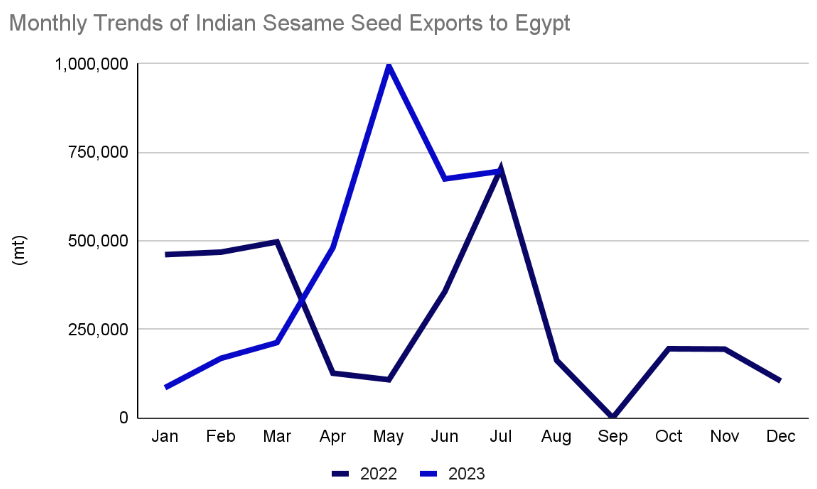
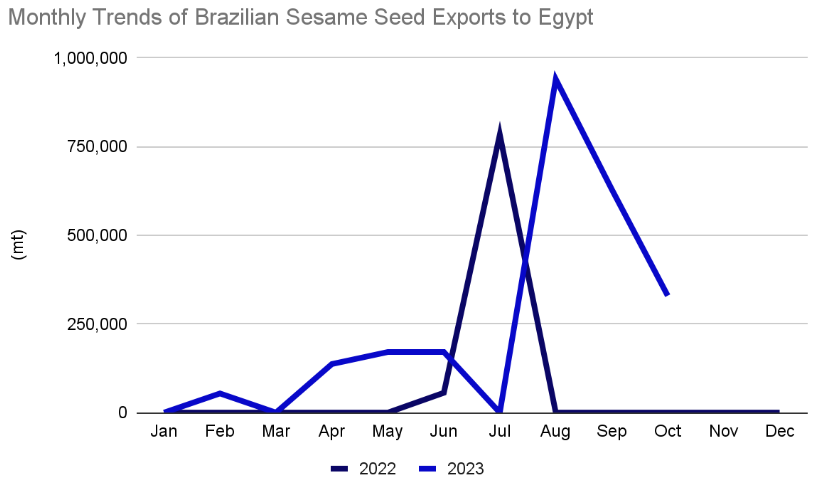
Moreover, the migration of the Sudanese community to Egypt, driven by ongoing conflicts, is expected to contribute to an increase in the consumption of sesame seeds within the country. We predicts persistent challenges associated with Sudan’s inability to produce sesame seeds, combined with the expanding Sudanese community in Egypt, leading to a heightened demand for Egyptian sesame seed imports. This underscores the ongoing imperative for Egypt to explore alternative sourcing strategies beyond Sudan.
India and Brazil, as alternative suppliers, collectively accounted for 11% of Egyptian sesame seed imports in 2022, indicating a rise in the sesame seed supply to Egypt. India experienced a notable 21.76% year-on-year increase, exporting 3,311 metric tons of sesame seeds to Egypt from January to July 2023, while Brazil’s exports surged by an impressive 189% year-on-year, reaching 2,432 metric tons from January to October 2023. Despite Egypt’s endeavors to enhance local sesame production, we anticipates the persistent absence of Sudan’s sesame market, influencing the Egyptian sesame seed industry. Consequently, Egypt must proactively diversify its sourcing channels to effectively boost sesame seed supply in 2024.
Israel functions as a net importer of fresh produce, with India playing a limited role as a supplier of cereals and oilseeds. The country’s imports have grown at a rate of two percent annually, constituting over 50 percent of its total agricultural produce supply. The major agricultural imports comprise cereals, accounting for approximately 26 percent, and oilseeds, constituting around 10 percent.
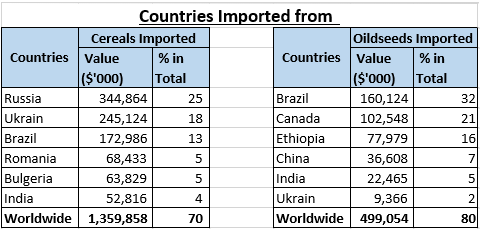
In the realm of agricultural imports, European countries play a more significant role compared to India. India’s involvement in supplying agricultural products to Israel is minor. Furthermore, in terms of exports, Israel is ranked 36th for cereals and 21st for oilseeds globally. India predominantly exports these products to regions such as Asia, Europe, and North America.
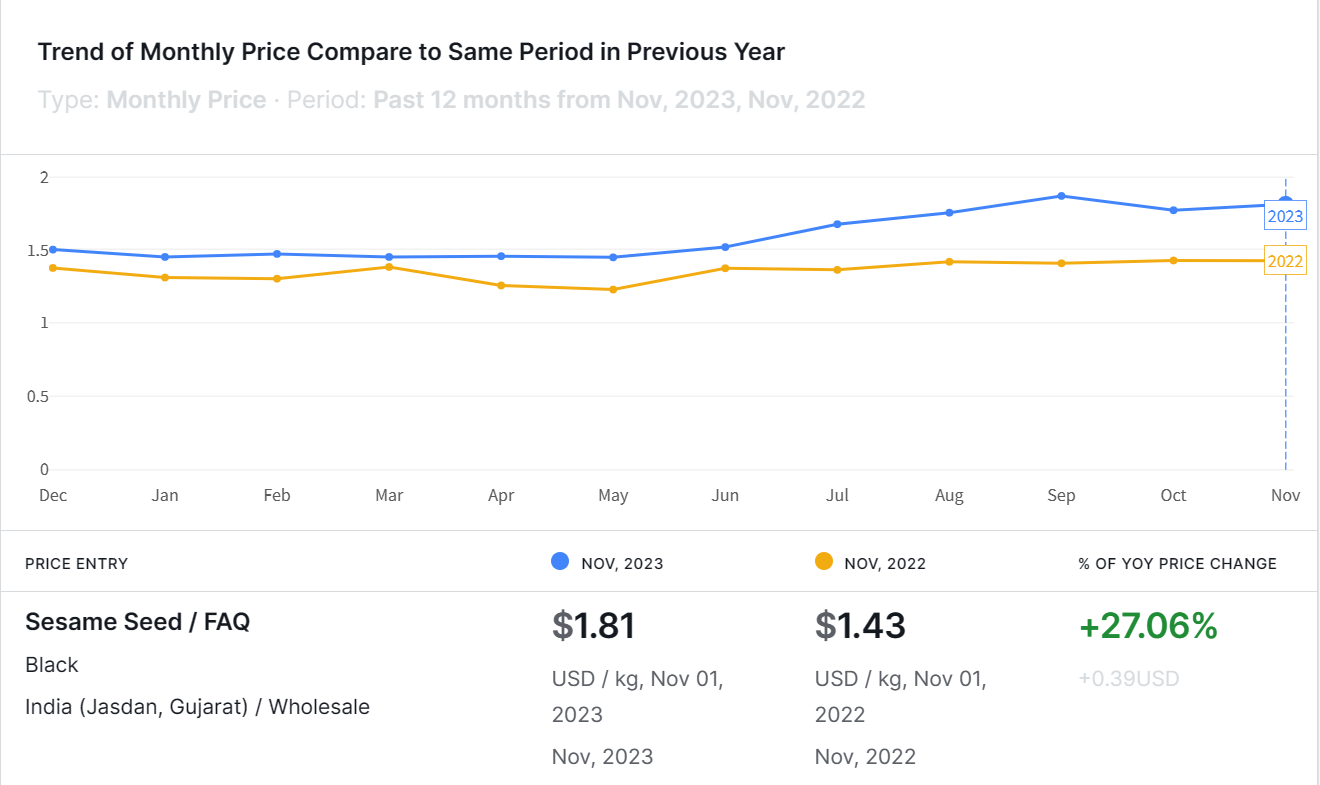
In December 2023, the prices of sesame seeds in India rose by 27.06% year-on-year, reaching USD 1.81 per kilogram. This surge can be attributed to supply shortages in key producing nations and heightened demand from the export market, with a particular emphasis on China. Additionally, apprehensions about crop losses resulting from climate change are expected to exert continued upward pressure on prices.
The wholesale price of sesame seeds in Gujarat, India, witnessed a year-on-year increase of 27.06% to reach USD 1.81 per kilogram in Week 49. Throughout the year 2023, sesame prices in India have consistently surpassed the levels recorded in 2022, displaying minimal fluctuations as of June 2023.
Several factors contribute to the escalation of sesame seed prices in India. A primary driver is the supply shortage in key producing nations in Africa, including Niger, Mozambique, and Tanzania. These countries have faced reduced production due to severe droughts linked to the El Niño phenomenon, resulting in a global upswing in sesame seed prices. The demand from the export market, notably from China, has also played a role in the price surge. Despite a decrease in China’s sesame seed import volume in 2023, the existing demand-supply gap is anticipated to persist, continuing to drive imports and uphold prices.
Moreover, India is grappling with a setback as sesame arrivals fall short of expectations. In Week 48, only 472 metric tons of sesame seeds were delivered to the trade market. The ongoing concerns about the impact of climate change on production are expected to maintain an upward trajectory in prices.
The continuing conflicts in the Middle East have wide-ranging impacts that resonate across the global business arena. It is crucial for companies to remain well-informed, adjust to evolving conditions, and deploy effective risk management strategies. Through vigilant monitoring of geopolitical events and maintaining adaptability, businesses can enhance their ability to navigate the challenges posed by the Middle East’s dynamic environment and sustain success in an ever-interconnected world.
The strait serves as a possible bottleneck for agricultural supply chains, witnessing the transit of over 50 million tonnes of agricultural products annually. In a broader context, the shipping industry is susceptible to increased costs if rising security concerns prompt shipping companies to reroute their operations.